Quality metrics are measuring quality standards and parameter; an organization track all the quality metrics for its improvement. Quality metrics will give clear data on where have quality measuring factors are. Quality metrics of the garments industry include many quality performance factors like customer complaints and return, DHU, In-process defects, sample pass rate, supplier performance, Final audit pass rate, Defects rate, and many others.
Difference between Metrics and KPI
Quality metrics are all quality measuring parameters and KPI is a key performance parameter among all metrics. KPI directly heat on overall company performance and metrics do not fully heat on overall performance. All quality KPI is in quality metrics, but all quality metrics are not in KPI. Let’s think about a football team, 11 players are playing the infield in the same team. From Messi, Ronaldo and two other players have key roles in the striking opponent goal post. So all 11 players are metrics and key 4 are KPI as well.
List of Quality Metrics and KPI’s used in the Garments/ Apparel industry
- Customer complaints
- Customer product Return
- AQL levels
- Percentage Defective level (DHU)
- Sample pass rate to customer
- In-process Defect
- Right First Time (RFT)
- Fabrics recut and wastage cutting department
- Marker Efficiency
- Rejection Rate: Rejection rate is a very important factor for quality control.
- Supplier quality performance
- Measurement Control and rejection Rate
- Rejection Rate in washing
- Submitted quality level (SQL)
- Outgoing quality level (OQL) or AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level)
- Final Inspection RFT/ Pass rate:
- Cost of poor quality (COPQ)
- Overall Customer satisfaction/ Customer Ratings
Description of different quality metrics and KPI of Garments industry in the following
Customer complaints
Customer complaints are a major concern for any industry, so the first thing you need to control is customer complaints. Customers pay for every product they get, so the expectation is to get a 100% good product. Customer complaints are the first point in any quality metric.
Customer Product Return
In some cases, customers return samples to the garment manufacturers to show the defects which not re-workable. Returning products to garments manufacturers is the worst thing for any maker.
AQL levels
The garment industry can focus on tightening the AQL level gradually to ensure the quality level is improving as AQL inspection is the shortcut of 100%. So AQL level comes into quality metrics.
Percentage Defective level (DHU)
Section-wise DHU (Defects per hundred unit) rate defines the respective section’s output quality. Garments manufacturer daily monitor cutting DHU, sewing DHU and finishing DHU. DHU is an important KPI for the garments industry. DHU is telling the % of defects at the end stage of any section.
Sample Pass Rate
A sampling pass is a way to do an order or ship a bulk order. To proceed new order, the garments maker has to submit a sample first and get approval from the customer. And some sampling requirements also for bulk old running production as well. Failing samples on the customer end are made a bad impression on garments manufacturers.
In-process Defect
Here I mean the In-process stage is different sewing machine-wise defects, having quality control in the process makes a good quality product. To reduce in-process defects, garments manufacturers can follow a traffic light system for every sewing or have roaming QC in the sewing line to roam everywhere and inspect.
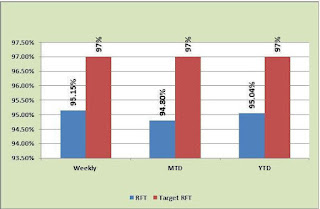
Right First Time (RFT)
RFT is the vice versa of defects %, anything garments maker make should be right at the first time. RFT cane measured on sample RFT rate, final inspection, etc. For sampling and Final inspection pass rate, the RFT target should be 98% or above in the garments industry.
Fabrics recut and wastage cutting department
Though fabric defect is a supplier defect that hampers cutting efficiency; the less recut percentage is, the more efficient cutting section will be.
Marker efficiency
Marker efficiency defines how much fabric is utilized in the cutting section. Always should have a target as much as possible.
Rejection Rate
Rejection rate is a very important factor for quality control. Garments rejection occurs for only quality problems. Rejection rate is one of the key performance metrics in the garments industry. Apart from the washing rejection, the in-process working error is the cause of rejection.
Supplier quality performance
Garments manufacturers only do cutting, sewing, and finishing; raw material supply by 3rd party. Garments manufacturers have the responsibility to inspect them and give clearance before using them. All garments manufacturers must have to control their supplier material quality, all trims, and accessories items and fabric must have to be qualified for use in garments manufacturing.
Measurement Control and rejection Rate
A garments buyer never accepts a product that does not meet measurement specifications. The is a big challenge for every garments manufacturer to keep control measurement with the customer specification. Lots of factors behind the measurement control like washing, sewing process, and many others.
Rejection Rate in washing
Among all rejection occurring in garments manufacturing, washing leads it from the top, especially in denim products. Garments damaged during the wash and coming shade variation from the buyer standard are two main reasons for washing reject.
Submitted quality level (SQL)
The level of defects with the product submit to customer QC for final inspection is called submitted quality level (SQL), whether the defects rate is acceptable to pass or not.
Outgoing quality level (OQL) or AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level)
In a garments industry, zero percent defect is almost impossible, so everywhere has an acceptance quality limit (AQL) that ensures a certain limit of satisfaction to the customer. For example, 5% of defect is accepted in AQL inspection. A customer observed a 4.5% defect in the final inspection, which is under the limit; we can tell Outgoing quality level (OQL) or AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level) is 4.5%. In one word, the percentage of defects sent to customers is called Outgoing quality level.
Final Inspection RFT/ Pass rate:
A buyer’s final inspection result is the ultimate inspection certificate for a vendor to deliver goods. The final audit pass rate is garments manufacturer performance that also counts customer as well. Failing in final inspection gives a bad impression to customers as customer representatives do an only final inspection in the garments factory.
Cost of poor quality (COPQ)
Cost of quality (COQ) is defined as the cost of having poor quality in a garment’s product. It is a methodology that allows the garments manufacturer to determine the extent to which its resources are used for activities that prevent poor quality, that appraise the quality of the organization’s products or services, and that result from internal and external failures. Having such information allows a company to determine the potential savings to be gained by implementing process improvements. Knowing COPQ will encourage the industry to minimize defects and increase the right-first-time product.
Overall Customer satisfaction/ Customer Ratings
Overall customer satisfaction is the key thing for any garments manufacturer. Only two ways you can satisfy buyer/ customer, one is on-time delivery and another one good quality. If a buyer is happy with the supplier’s garment quality, then nothing more needs to do for a supplier. Product consumers/ customers give ratings online, rating is a big factor for any business.
Among all the quality metrics, some quality parameters come under KPI. To be a successful garments manufacturer, these quality metrics factors have to be monitored regularly.