Different Actions of Carding Machine in Spinning (Yarn Manufacturing) Process
The carding machine is called the “Heart of the spinning”. It is also said that “Well card is half spun”. Becasue Yarn manufacturing process is impossible without carding. And, It has the key functions in the manufacturing process. Carding is the first process which is dedicated to individualizing the fibers. Carding is done just after the operations in the blow room. Blowroom lap is fed and card sliver is received as the output. This whole carding process combines different kinds of actions. Some basic actions of this carding machine are Combing action, Carding action, Stripping action, and Doffing action. There are more within these actions themselves. So let us dive deeper and acquire some information about the core of the carding machine’s actions.
What is a Carding Machine?
A carding machine is a textile processing machine that produces a thin web of wool, cotton, or other fibers by individualizing, disentangling, and aligning the fiber strands. After that, this web is further processed into thread or yarn for use in textiles. The carding machine also includes a cleaning mechanism to clear any impurities from the fibers as they pass through the rollers, such as dirt or debris. This assures that the carded sliver is of high quality and free from any imperfections.
Why do we need to use a Carding Machine?
The quality of the final product of the spinning line-up which is the yarn heavily depends upon the efficacy of this carding machine. We can figure out some critical reasons that heavily impact the yarn manufacturing process.
- Fiber preparation: Wool, as well as cotton, are examples of raw fibers that are usually inadequate for spinning into yarn without some sort of preparation. By opening up the fibers, cleaning them of any impurities, disentangling, mixing, and aligning them into a thin web, the carding machine facilitates the preparation of the fibers.
- Uniformity: The carding machine assures that the fibers are processed evenly, which leads to the outcome being consistent. This is crucial to maintaining the finished textile’s quality and ensuring that it performs as expected.
- Cleaning: This machine ensures maximum cleaning. The blow room removes around 50-60% of impurities but further cleaning is required. Dust is turned into micro-dusts in this machine. 90% of the remaining impurities are processed here into micro-dusts.
- Mixing: Different fiber types can be mixed using a carding machine to produce a special blend with distinct properties. As a result, manufacturers can produce textiles with particular qualities like softness, durability, or other functionalities.
- Effectiveness: The carding machine is highly automated and capable of rapidly and efficiently processing large amounts of fibers. By doing so, production rates are raised while manufacturing expenses are decreased.
Overall, the carding machine is an important factor in the textile production process because it assists in making preparations for the raw fibers for further processing and assures the high quality and consistency of the final product.
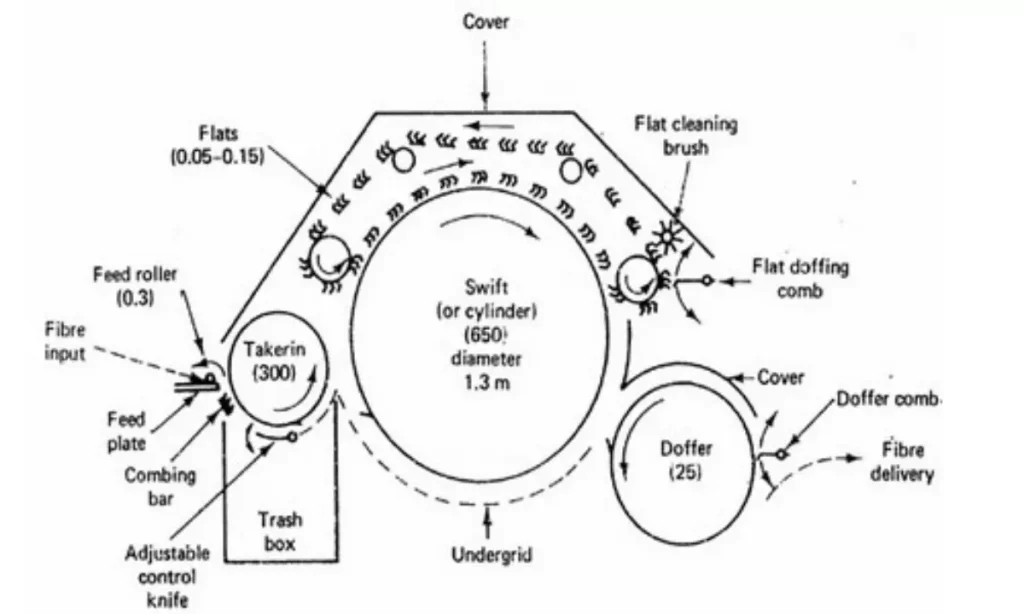
What are the actions of the Carding Machine?
The carding machine performs some actions to align, clean, mix, and turn into a suitable even form for a good quality card sliver. The machine takes various actions simultaneously. Some basic actions which are considered to be a must for a better outcome are described here:
Combing Action
The term combing refers to parallelization and individualization of the material which is blow room lap in the case of this machine. The combing process involves passing the carded fibers through a machine with fine-wired combs that remove short fibers and any remaining impurities. This process results in a more even and uniform fiber length and removes any remaining impurities.
Combing Zone
Combining action takes place between the feed roller and taker-in rollers. The feed roller is fluted which is mainly designed to hold the grip on the material and the taker-in roller surface has metal wires for combing.
Purposes of Combing Action
- Opening the material into micro-tufts
- Fiber individualization
But the blow room lap does not meet the conditions required for a better yarn. That is why combing is a must for yarn manufacturing.
Mechanism
- The material is fed to the taker-in by the feed roller.
- The feed roller and the taker-in roller rotate in the opposite direction.
- The wired surface of the taker-in roller pulls the fibers and aligns them in order.
- Individualization is also done at the same time.
- The higher surface speed of the taker-in roller pulls materials quicker than the feeding ratio and passes a comparatively aligned material to the next step.
Carding Action
Carding is the process of turning tufts of fibers into micro-tufts and individualizing, blending, and orienting them in a manner. This action serves the principal purpose of using the carding machine.
Carding Zone
Carding action takes place between the card cylinder and the flat bars. The surface of the card cylinder consists of many fine wires that are designed in the opposite direction of the flat brushes which have a bent pin-like structure.
Purpose of Carding Action
- Individualizing the fibers
- Cleaning the fibers
- Disentangling the fibers
- Orienting the fibers partially
- Mixing/blending the fibers
- Removing neps to a certain point
Mechanism
- The card cylinder collects materials from the taker-in
- The card cylinder rotates and comes in contact with revolving flat bars that have blat brushes.
- The wires of the card cylinder and flat brushes rotate in the opposite direction. As a result, the fibers get attached to the flat bars and perform the carding action.
- Later on, the materials are stripped from flat brushes by a stripping roller
Stripping Action
The term refers to detaching fibers from one cylinder or roller and delivering them to the next part of the machine. The process of removing fiber waste and impurities from the carding machine’s main cylinder or drum can be referred to as stripping action in the carding machine
Stripping Zone
Stripping action takes place between the
- Taker-in roller and card cylinder
- Doffer and 1st stripping roller
Generally stripping action occurs in these 2 portions of the carding machine
The wired surface of the doffer is less dense than the card cylinder and the surface of the 1st stripper roller’s surface has a coarser wired surface.
The taker-in roller and the card cylinder rotate in the same direction but the direction is opposite in the case of the doffer cylinder and 1st stripper roller.
Purpose of Stripping Action
- Stripping fibers from the taker-in roller and doffer cylinder
- Delivering fibers to the next rollers
Mechanism
In the first case:
- The taker-in roller and the card cylinder rotate in the same direction but the design of the wires are designed in the opposite direction than the other.
- The fibers thus get detached from the taker-in to the card cylinder
In the second case:
- The doffer cylinder and the 1st stripping roller rotate in the same direction also but the direction of the wires on the surface is reversed if compared with the other cylinder.
- When the cylinders rotate, the fibers get detached like in the previous mechanism.
Doffing Action
Doffing Zone
Doffing action takes place between the card cylinder and the doffer cylinder. The wires of the surface of the cylinders are designed in a relatively opposite direction but both of the cylinders rotate in the same direction.
Purpose of Doffing
- Detaching fibers from the card cylinder by the doffer cylinder
- Collecting individualized fibers from the card cylinder and turning them into card web
Mechanism
- The card cylinder and the doffer cylinder rotate in the same direction
- But relatively opposite in direction, the wires of the doffer cylinders collect individualized fibers from the card cylinder
- The surface speed of the doffer cylinder is faster than the card cylinder. As a result, a condensed web is formed named card web
Closure: That is all on the topic. Hope that everything is covered in this article.
- You may love to read: Difference between Yarn and Thread
- Nylon Drawn Textured Yarn – DTY: Basic Information
- Textile Testing: Fiber, Yarn, Fabric, and Garments test
- Author: Md. Sharuzzaman Chawdhury
- Textile Machinery Design & Maintenance
- Bangladesh University of Textiles


