Recent Developments in Medical Textiles
Introduction
Medical Textile is one of the most important category of technical textiles. The primary requirements for medical textiles are that they are biocompatible and comfortable. Medical textiles are used to protect healthcare professionals from containment fluids. Doctors, textile chemists, and technologists all use Meditech materials. The classification of medical textiles into four categories—health and hygiene, extracorporeal devices, implantable materials, and non-implantable materials—gives this article a thorough overview of this area of textiles. Additionally, each class and product are described along with how they are used. Medical textiles fill a specific market need by using cutting-edge methods to promote human health. Medical textile growth is currently 7%, which is respectable, but it is predicted to soar in the coming years. We are discussing here Recent Developments in Medical Textiles.
What is Meditech?
Meditech is a short form for Medical Textiles. It is a new field created through the fusion of textile technology and medical sciences. With the creation of new fibers and yarn and fabric manufacturing techniques, new medical textile applications have been found. All textile items that improve human health and well-being, shield us from disease and infection, support injured limbs externally, hasten wound healing, and replace diseased and damaged tissues and organs are included in the expanding field of medical textiles. Medical textiles are fiber-based structures or textile products used in the medical field for the treatment of any medical condition.
Properties of Medical Textiles
Specially designed textile-based products with medical applications are made from medical textiles. These items are used for hygiene, care, and prevention. The following qualities must be present in the materials used to make medical textile products:
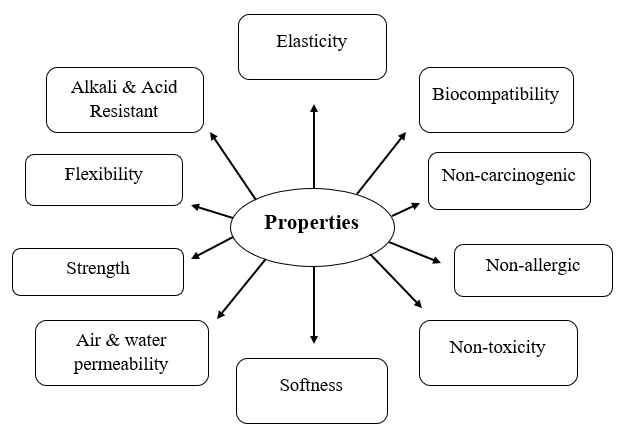
Why Medical Textiles?
Tissues now have a significant role in the treatment of wounds and the prevention of chronic wounds. Medical textiles need to be durable, flexible, and biocompatible. Improved airbag on dressings offers greater comfort when dressing wounds. Innovative superabsorbent polymers like sodium acrylate and polyacrylate increase the absorbency of fibers. Recent advancements and particular requirements necessitate the development of novel surgical sutures, such as serrated-toothed gut sutures coated in gelatin. snake in the goat’s breast. The use of monofilament, multifilament, woven, and non-woven textile materials for biological and medical purposes has sparked a lot of interest in the field of medical technology.

Types of Fiber Usedin Medical Textile
The choice of fiber for medical use is made based on the use for which it is intended. Fibers are primarily chosen based on their biodegradability or non-biodegradability as well as the other attributes mentioned above. In the medical and healthcare fields, a variety of fabrics are used such as;
- Woven fabric
- Non-woven fabric
- Knitted fabric
- Braided
However, woven and non-woven fabric is used to create the majority of medical textiles.
| Fibers | Biodegradable | Applications |
| Cotton | Yes | Surgical hosiery & gowns, uniforms, bedding, sheets, and pillowcases, among other things. |
| Viscose | Yes | PPE, plasters, bandages, caps, masks, wipes, wound care pads, etc. |
| Hollow viscose | Yes | Artificial Kidney. Artificial Liver. |
| Polyamide | Yes | Artificial tendons, Artificial bones, etc. |
| Polyester | No | Gowns, surgical draping materials, blankets, cover stock, surgical hosiery, sutures, artificial tendon, etc. |
| Hollow polyester | No | Artificial Kidney. |
| Polypropylene (PP) | No | Surgical hosiery, Bandages, Wound care pad, etc. |
| Polyethylene (PE) | No | Protective Clothing, Sutures Plasters, etc. |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | No | Caps, Masks, Plasters, etc. |
| Glass | No | Artificial tendons, Artificial bones etc. |
| Carbon | No | Surgical hosiery, Gloves, etc. |
| Collagen | Yes | Artificial skin, Ligament, Lumen, Sutures |
| Elastomeric | Yes | Surgical hosiery, Gloves etc. |
| Polylactic acid | Yes | Implants such as naturally dissolving stents. |
| Polyglycolide | Yes | Absorbable synthetic braided multifilament. |
These fibers are further subdivided into two categories:
Specialty fibers – These types of fibers include Chitosan, Chitin, Collagen, and calcium Alginate fibers.
Commodity fibers – Natural fibers and synthetic fibers are the two additional classifications for commodity fibers. Natural fibers used in hygiene products and non-implantable materials include silk, cotton, and viscose In contrast, the synthetic fibers include polyamide, polypropylene, PTFE, and carbon.
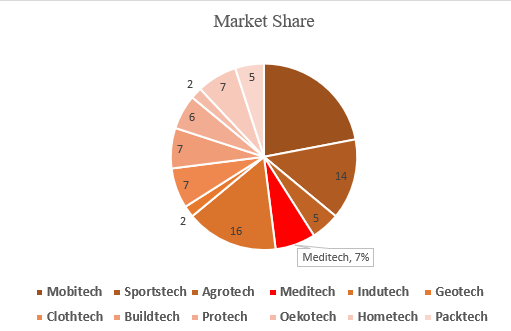
Based on product characteristics, functional requirements, and end-user applications; technical textiles products have been classified into 12 categories, viz., Agrotech (Agro-textiles), Buildtech (Construction Textiles), Clothtech (Clothing Textiles), Geotech (Geo-textiles), Hometech (Domestic Textiles), Indutech (Industrial Textiles), Mobiltech (Textiles used in transport; automotive and aerospace), Oekotech (Ecological Protection Textile), Packtech (Packaging Textiles), Protech (Protective Textiles), Sportech (Sports Textiles) and Meditech (Medical Textiles).
Among all these sectors Meditech has a share of 7% and it is still growing. So developments in Medical Textiles are very important.
By 2028, the market for medical textiles is anticipated to be worth USD 26.21 billion. From 2021 to 2028, it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.5 percent. Over the course of the forecast period, the market growth is anticipated to be supported by the emergence of new medical textile application areas as well as the development of novel fibers and yarn and fabric manufacturing technologies. Let’s talk about the Recent Developments in Medical Textiles.
APPLICATION AREA
Classification of medical textiles:
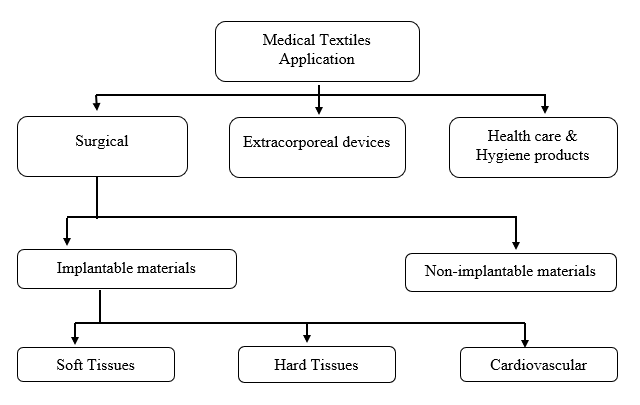
Developments in each area of Application of Medical Textile
Product category wise Recent Developments in Medical Textiles points are given.
1. Healthcare & hygienic products:
It includes surgical textiles, barrier products, surgical caps and gowns for nurses, breathable membranes, footwear, and clothing, among other things. These products’ primary purpose is to shield medical personnel from contact with potentially infectious fluids, such as blood.
Operating Theatre
Surgical uniform – The operating room’s environment must be spotless, and infection control must be strictly enforced. The nursing staff’s pollutant particle, which contains bacteria, could be a source of infection for the patient. To stop pollutant particles from being released into the air, surgical gowns should act as a barrier. Disposable non-woven surgical gowns, which are frequently made from a composite material of nonwoven and polyethylene films, have been adopted to stop these sources of contamination for patients.
Surgical masks – should be allergy-free, lightweight, and have a high level of air permeability.
Surgical caps – these are created from cellulose-based nonwoven materials to protect the patients from the risk of hair falling into the sterile area during surgery.
Surgical drapes and cover cloths – These are used to drape working spaces around patients or to cover the patients themselves. It is a sterile drape used to cover the body while surgery is being performed. Being they are low lint they make a great wipe to clean sterilized surgical instruments. They can also be used in surgery to cover certain areas of the patient.
Hospital Ward
Sanitary Napkins: Sanitary napkins are made of three layers of textiles used in medical applications. Wool makes up the inner layer that comes into contact with the body. The inner layer must possess some unique qualities, like portability. Blood flows quickly during menstruation from the inner to outer layers, and the inner layer is comfortable, elastic, and blood-resistant. The sanitary napkin’s inner layer is made of a unique polymer with exceptional absorption capabilities. Polyethylene is used to create the outer layer.
Calcium Alginate Fibres – Alginic acid, a substance obtained from marine brown algae, is used as the primary raw material for making this fiber. It has a variety of qualities, including the capacity to gel, form layers of film, and stabilize viscous suspension. The reverse ion exchange occurs when the dressing made of this fiber is applied to the wound. This fiber is placed on the wound in a dry state and starts to absorb the exudates. The sodium ions that are present in the blood and wound exudates are gradually exchanged for the calcium ions.
Thin film dressing – There has been the development of a better thin film dressing with an absorbent border. While maintaining the conformability of a thin layer and a support layer, the dressing has a superior ability to quickly absorb bodily fluid, prevent dressing leakage, and prevent wound maceration. Any appropriate bonding technique, such as adhesive heat or ultrasonics, is used to attach the support layer to the occlusive layer and another layer.
2. Extracorporeal devices:
When vital organs aren’t functioning properly, this kind of medical textile is used in its place. Typically, hollow fibers such as viscose hollow, and hollow polyester are used to create these devices.
Artificial kidney – It is small, similar in size to a two-cell flashlight, made from hollow polyester or cellulose fibers that are slightly larger than capillary vessels but smaller than hair. A bioartificial kidney is developed that consists of a blood filtration unit (called the hemofilter) and human kidney cells (called the bioreactor).
Artificial liver – In order to help the diseased liver until it regenerates or until a suitable graft for transplantation is available, plasma is circulated over living, functionally active hepatocytes packed in a bioreactor. It is made of hollow viscose to separate and dispose of patient’s plasmas and supply fresh plasma.
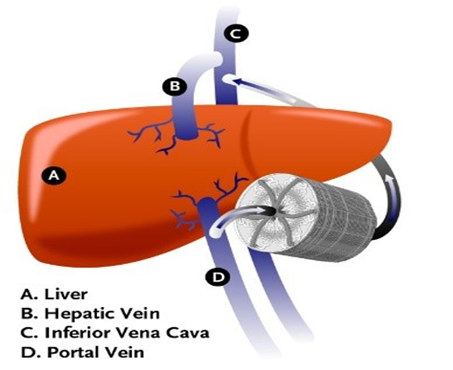
Artificial heart – An eight-ounce plastic pump with chambers about the size of the human heart that is covered in decor velour to prevent blood damage. Unwanted blood gas cannot escape from the fabric thanks to its Silastic backing.
3. Implantable materials:
These biocompatible medical textiles are made to be used inside the human body. Implantable materials can be used for a variety of restorative purposes, including the replacement of damaged heart valves, blood vessel replacement, wound closure, and artificial skin replacement.
For instance: Sutures, Soft tissue inserts, Orthopaedic inserts, cardiovascular inserts, and so forth are utilized in materials.
Surgical Sutures – A suture is the most frequently implanted bio textile device. They are used to close the wound when tissue separation happens as a result of an incision, puncture, abrasion, or other injury. Sutures are any materials used to stitch together damaged bodily tissues and keep them in the right positions while healing occurs. Sutures are used to join various types of tissues during surgery and are becoming more and more common in the field of medical textiles. Wounds are stitched shut using knot and barbed sutures, both of which are relatively new.
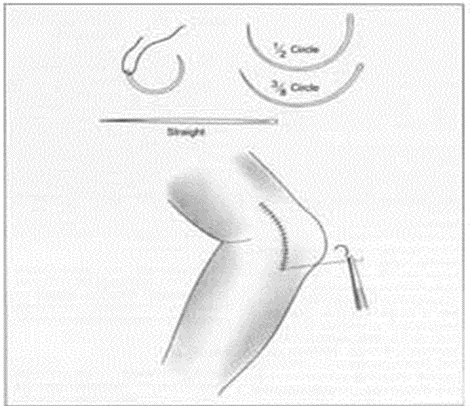
Vascular prosthesis – In 1956, a polyamide fiber-based vascular graft was created for the first time. Polyamide was quickly replaced by polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) fiber, and then polyester fiber was introduced. A variety of synthetic materials are used to create the implants. The two main fibers are polyester and PTFE. Polyacrylonitrile and polypropylene. However, the most popular vascular prostheses currently available are made of polyester and PTFE.
4. Non-implantable materials
These materials are used for external applications on the body and may or may not make contact with the skin. They are made from a co-polymer of two α amino acids.
This includes wound care, bandages, plasters, pressure garments, orthopedic belts, etc.
Surgical dressing
Primary wound dressing – This includes the subsequent products: To avoid wound adhesion or fiber loss, wadding is a high-absorbency material that is covered in non-woven fabric. Lint: Lint is a simple cotton fabric with a plain weave that is used as a dressing to protect minor burns. Gauze is an open-weave, absorbent fabric with a paraffin wax coating that is used to treat burns.

Antimicrobial Wound Dressing – Kerlix AMD is pure cotton that has been given a polyhexamethylene biguanide treatment by Anecia. These antimicrobial substances prevent bacteria from growing inside the dressing and from penetrating through the product. The material used to cover wounds is hydrophobic, bacteria-adsorbing, and contains an antimicrobial active ingredient that is not released into the wounds. It is preferably a blend of hydrophobic and antimicrobial fibers.
Absorbent – Super-absorbent materials, commonly referred to as super-absorbent polymers or SAP, are made of substances that can absorb a great deal more water than their own weight. As the diameter grows, super-absorbent fibers can absorb 50–150 times their own weight. The fiber has a very large surface area for contact with the liquid due to its small diameter of 30 m. They are excellent materials for items like feminine hygiene pads and liners, incontinence products, and infant diapers and nappies that are intended to contain fluids.
Bandages – There are many uses for bandages, which help to keep the dressing on the wound. Bandages can be knitted, woven, or nonwoven; knitting with warp and weft creates tubular structures. It can either have an elastic or inelastic nature. The bandage structure is made more comfortable and supportive by the elastic yarn.
Compression Bandages – Bandages’ primary purposes are compression, retention, and support. This is accomplished through inherent component characteristics that are further strengthened and reinforced by weaving and finishing techniques appropriate to the desired end-use.

Adhesive tapes – Instead of using fasteners, screws, or welding to join or bond objects together, adhesive tapes combine material with an adhesive film. Another good part of Developments in Medical Textiles.
The below table illustrates the application of all the categories mentioned above:
| Product Application | Fibre Type |
| Healthcare & hygienic products | |
| Surgical clothing gowns | Cotton, Polyester, Viscose rayon, Polypropylene |
| Surgical covers drapes cloth | Polyester, Polyethylene, Polyester, Polyethylene |
| Beddings | Cotton, Polyester |
| Blankets, Sheets | Cotton |
| Pillow covers | Cotton |
| Protective clothing | Polyester, Polypropylene |
| Cloths/ Wipes | Viscose rayon |
| Surgical hosiery | Polyamide, Polyester, Cotton, Elastomeric yarns |
| Extracorporeal devices | |
| Artificial Lungs | Hollow viscose |
| Artificial Kidney | Hollow viscose, triacetate, polyvinyl alcohol, polyester |
| Artificial Blood Vessel | PET fabric or Polytetrafluoroethylene membrane |
| Implantable materials | |
| Sutures | Carbon fiber |
| Soft-tissues | Polytetrafluroethylene fibre, polyester fibre, polyamide fibre silk |
| Artificial Ligaments | Polyester and collagen |
| Artificial Skin | Silicon/Nylon, polypeptides |
| Artificial Bones | Carbon fibre |
| Vascular grafts | Polytetrafluroethylene fibre, polyester fibre |
| Non-implantable materials | |
| Wound care absorbent pad | Cotton, viscose silk, polyamide fibre viscose, polyethylene fibre viscose plastic film |
| Bandages | Cotton viscose polyamide fibre |
| Wadding | Viscose cotton, linters, wood pulp |
| Lint | Cotton |
Companies Manufacturing Medical Textile in India & in the world
Some worldwide companies that manufacture medical textiles are:
- Atex Technologies, Inc.
- Life-Threads
- Careismatic Brands
- Bally Ribbon Mills
- Freudenberg & Co. KG
- Trelleborg AB
- Indorama Corporation
- Herculite
- PurThread Technologies, Inc.
- Fitesa
A few Indian companies that manufacture medical textiles are:
- Aalay Surgicals Pvt. Ltd.
- Abaan Packaging
- Abi Safety Wears Industries
- Adarsh Synthetics Private Limited
- Agro Biotech International Exports Private Limited
Conclusion
Medical textiles play a huge role in improving health and quality of life for people. The creation of new products and technologies will assist patients in overcoming the difficulties they previously faced. There are a lot more unexplored facets of medical textiles; we ought to look into them. The creation of healthy and top-notch medical textile materials requires more focus. In addition to technology, we also need to pay attention to how much our goods cost in the Recent Developments in Medical Textiles. This will make it possible to create high-quality, fully functional, and easily accessible modern medical textiles.
- References:
- https://www.technicaltextile.net/articles/medical-textiles-2587
- https://textiledetails.com/application-of-medical-textile/
- https://textilelearner.net/medical-textiles/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medical_textiles
- https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3736927/medical-textiles-market-size-share
- https://www.indiantextilemagazine.in/india-an-emerging-market-global-manufacturing
- https://www.textilesphere.com/2020/03/medical-textiles.html
- https://www.fibre2fashion.com/industry-article/1466/recent-developments-in-medical-textiles
- https://www.technicaltextile.net/articles/medical-textiles/27?page=2
- https://www.jasonmills.com/blog/medical-textiles/
- https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/medical-textiles-market
- You may love to read: Classification of Medical Textile
- Overview of Medical Textile
