Knitting is a fabric process that produces knit fabrics. The process of interlocking loops of yarn, using one or more needles. Knitted fabrics can be stretchy, warm, durable, and comfortable, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Knitting is also an enjoyable and relaxing hobby for many people. Generally, Knitting is two types; Warp Knitting and Weft Knitting. Warp knitting and weft knitting are two different Knitting techniques used in the production of knitted fabrics.
Warp Knitting
In the warp knitting process, the yarn is fed into the knitting machine in a vertical direction, perpendicular to the direction of the fabric being produced. The yarn is held under tension and is interlocked with itself to form the fabric. Warp knitting is used to produce fabrics that are stable, have good dimensional stability, and are resistant to runs or snags. Examples of fabrics produced by warp knitting include tricot, raschel lace, and double-knit fabrics. Produced fabrics and garments from the warp Knitting are Inner-wears (brassieres, panties, camisoles, girdles, sleepwear), apparels sweater, shoes, and many other items.
Weft Knitting
In weft knitting, the yarn is fed into the knitting machine in a horizontal direction, parallel to the direction of the fabric being produced. The yarn is interlocked with itself to form the fabric by passing over and under a series of loops. Weft knitted fabrics are knitted fabrics in which a yarn forms loops across the width of the fabric; they can be either hand-made or machine processed. Weft knitting is used to produce stretchy, flexible fabrics that have a softer, more draping hand feel. Examples of fabrics produced by weft knitting include single-knit jerseys, rib knit, and interlock knit. Single and double Jersey fabrics are produced in the weft knitting process.
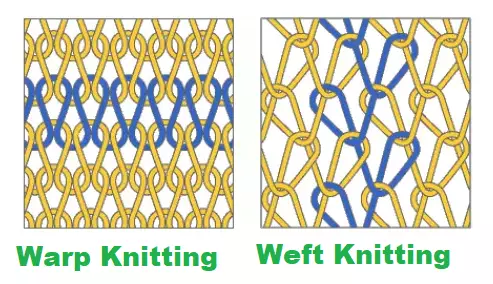
Difference between Warp Knitting and Weft Knitting
| SL No. | Warp Knitting | Weft Knitting |
| 01 | Here, the used yarn runs in the vertical direction. | Here the used yarn runs in the horizontal direction. |
| 02 | Warp knitting is elastic to the length. | This type of knitting is elastic to the width. |
| 03 | It has less shrinkage than weft knitting. | It has higher shrinkage than warp knitting. |
| 04 | Used yarns are supplied from the beam. | Here, used yarns are supplied from the cone. |
| 05 | Warp knitted fabric is too perfect for the dry wash. | Weft knitted fabric is perfect for hand wash. |
| 06 | Warp knitting is suitable for producing coarse fabric. | This type of knitting is perfect for producing thin fabric. |
| 07 | Here, the loops are produced to the length of the fabric. | Here, the loops are produced to the width of the fabric. |
| 08 | Yarn is held under constant tension | Yarn tension varies in the process |
| 09 | Elasticity is less for warp-knitted fabric. | Higher elasticity for weft knitted fabric. |
| 10 | More courses are required for each pattern raw. | Here, the course is equal to the pattern. |
| 11 | Here, at least one yarn is required for each knitting needle. | Here, any number of knitting needles is required for one yarn. |
| 12 | It’s easy to produce any kind of fabric design by using the warp knitting process. | It’s tough to produce any kind of fabric design by using this knitting process. |
| 13 | Warp knitting is raschel, made with latch needles, and tricot. | Weft knitting fabrics are single and double-knit jerseys, rib knit, and interlock knit |
| 14 | Warp knitting fabrics are Jersey, Interlock, Rib, Pique, Terry, French Terry, Fleece Knit, Tricot, etc. | Weft Knitting fabrics are Jersey, interlock, terry, valor, etc. |
Reference: https://garmentsmerchandising.com/warp-weft-knitting-textile-difference/
