Fabric Defect
There are many fabric defects generated in the weaving and knitting process and yarn has some defects as well that directly affect fabric quality. As fabrics are the main part of textile and apparel, knowing fabric defects or faults is important. Fabric is used directly in apparel and fashion, controlling fabrics is the first thing to do for any fabrics manufacturer. Nowadays, the fabrics manufacturer’s business depends on the level of defects in their fabrics. Clothing manufacturer always deals with good fabrics to make nice cloth like a jacket, shirt, pants, and others; even a readymade cloth get rejected for only a small fabrics defect. Fabric design defines the fashion of any clothing item.
Why do fabrics have defects/faults??
Few reasons for having defects in fabrics:
- Faulty yarn used for weaving and knitting; inconsistent yarn quality.
- Flying dust in the weaving and knitting section
- Weaving and knitting machine inefficiency
- Faulty settings of the machine.
- Excessive loom weaving machine tension and Loose tension.
- Improper fixation of weaving and knitting machine mechanism.
- Improper dyeing, printing, and finishing.
- Improper sizing and too many count variations.
- Other reasons.
Different types of fabrics defects by defects producing source:
Fabric defects generate in various stages from raw fabric manufacturing to finished fabric and poor yarn quality also plays a big part in fabric defects. Here is the list of defects produced in different stages of fabric. Here are given some examples, and defect details after this chart.
- Fabric Defects produced during manufacturing
- Finishing process defects of Fabric
- Printing process defects of fabrics
Fabric Defects produced during manufacturing :
- Broken Yarn
- Missing Yarn
- Color Yarn
- Slub
- Spot
- Big Thread
- Knot/Nap
- Line Mark
- Uneven Dyed
- Mispick
- Stop Mark
Finishing process defects of Fabric
- Burl Mark
- Crease Mark
- Hole
- Miss Print
- Joint / Splice
- Shade Bar
- Broken Selvage
Dyeing and Printing process defects of fabrics
- Bow/Skew
- Color Out
- Uneven Print
- Uneven Dye
List of Different types of fabric Defects
- Slub
- Knot
- Thick Yarn
- Thin Yarn
- Running Shade variation
- CSV- Center to selvage shade variation
- Miss Yarn
- Color Yarn
- Fabric Hand feel
- Hole
- Uneven Dye
- Uneven Print
- Foreign Yarn/ Contamination
- Crease mark
- Fabric Skew
- Fabric Bowing
- Stain/ Spot/ Dirt
- WaterMark
- Fabric Way
- Line mark
- Broken Yarn
- Bad Selvedge
- Loose warp
- Mispick
- Stop Mark
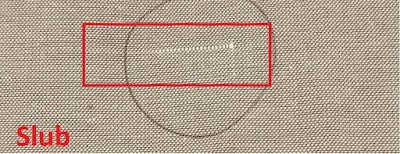
Slub
A slub is a thick place in the fabric, a slub in the fabric is a fault.
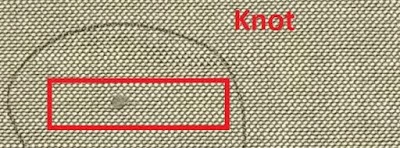
Knot
Very small tightly gathered unorganized thread and fiber together make a defect called a knot.
Thick Yarn
One thread in fabrics that is thicker than others, counts as a thick yarn defect.
Thin Yarn
In fabrics, if there one thread is thinner than all others, counts as a thin yarn defect.
Running Shade variation
Lengthwise shade variation the same roll is called running shade. Head, middle and the end of a roll should be same everywhere.
CSV- Center to selvedge shade variation
Fabric selvedge shade and center shade does not match roll edge; CSV is the opposite direction of running shade. CSV is width-wise shade variation. CSV shading increases the fabric consumption and reduces marker efficiency in the cutting section.
Miss Yarn
A yarn that is missing in a specific area of fabric is called a miss yarn.
Color Yarn
A contrasting yarn in the fabric is called color yarn or contrast yarn which color does not match the fabric color.
Fabric Hand feel
Every fabric item has a certain hand feeling, anything that deviates from the hand feeling is called a fabric hand feel defect.
Hole
A hole in the fabric is an incorrigible and critical defect, any hole found in the fabric is a defect to trace anywhere. A hole is a hollow place or opening in solid fabrics.
Uneven Dye
Dyeing should be done evenly all over the fabric rolls, any deviation from it is uneven dyeing. Dyeing is not done evenly throughout the fabric rolls is called uneven dyeing. Dyeing should be the same all over fabric areas as per approved shade and receipe.
Uneven Print
Similar to uneven dyeing, printing that is not placed evenly in the fabric is called an uneven print.
Foreign Yarn/ Contamination
Any yarn found that is inserted into the fabric from flying dust or another way, a yarn in fabric which not belong to fabric is called foreign yarn.
Crease mark
During dyeing, finishing, and other processes, some creases or folds create crease marks. Getting crease in fabric makes crease mark in fabric.
Fabric Skew
The weft yarn line is angularly displaced from a line perpendicular to the edge or side of the fabric due to the uneven distribution of tension.
Fabric Bowing
When filling yarns are displaced from a line perpendicular to the selvages and lie in an arc across the width of the fabric is called fabric bowing.
Stain/ Spot/ Dirt
Stain is any kind of spot, dust, dirt, or oil spot found in fabric. These defects are generated from any area like weaving, knitting, dyeing, finishing or packaging, etc. Improper handling is also a big reason for having spot in fabric
WaterMark
Having spots in fabrics for staying wet for some time, a watermark can be visible in the fabric.
Fabric Way
Every Fabric has a different structure to set grainline, fabric structure fix length, and widthwise grain line. Any deviation from it is called fabric way mistake or defect.
Line mark
Line mark is a Streaky mark found in fabric, especially we get it denim fabric. This defect is produced in the weaving and dyeing process.
Broken Yarn
Fabric is manufactured by yarn in weaving or knitting. Yarn having breakage in the fabric is called ‘Broken yarn’ defect. Mainly it happened for improper tension in weaving and knitting.
Bad Selvedge
Bad Selvedge is found in the woven fabric due to faulty weaving.
Loose warp
A loose warp is a type of warp produced in the woven fabric due to the tension looseness of the fabric.
Mispick
Missing one pick in the fabric is a ‘mispick’. If a weft or filling yarn skipped in a pick that is called “mispick”.
Stop Mark
This defect is the result of yarn elongating under tension during a loom stop. When the loom is restarted, the slackness is woven into the fabric. This is more common in polyester and polyester blends than in all-cotton.
Other defects of Fabric
There are many other defects in a fabric we see. Some of them are Double pick, splicing, horizontal lines, drop stitches, Misprinting, Barre, Abrasion marks, Snags, Needle lines, Coarse pick, Coarse end, broken pick, broken end, missing end, Filling bar, etc.