Sustainability is taken into account by many to be the grail of the style industry. Deciding way to create a cloth closed-loop and finding viable alternatives to clothing ending up in landfills, are the 2 biggest challenges currently facing the style industry. That’s why during this article we’ll check out materiality and the way we will use innovation and sustainability as an answer for contemporary fashion. This article is for understanding materiality and sustainability in clothing and fashion.
The world buys more and more clothing annually. This suggests we’re throwing out quite ever also. Erick Bang, project manager for the Global Change Award, a corporation sponsored by the H&M Conscious Foundation, put it, “Fashionista or not, clothes are a necessity, and one among the most important challenges facing today’s apparel industry is the way to create fashion for a growing world population while protecting our planet.”
How can we modify this?
Let’s check out five ideas given for a sustainable approach to materiality in the recent Global Change Awards competition.
What are Materiality and Sustainability in Fashion and clothing
1. Polyester eating microbes.
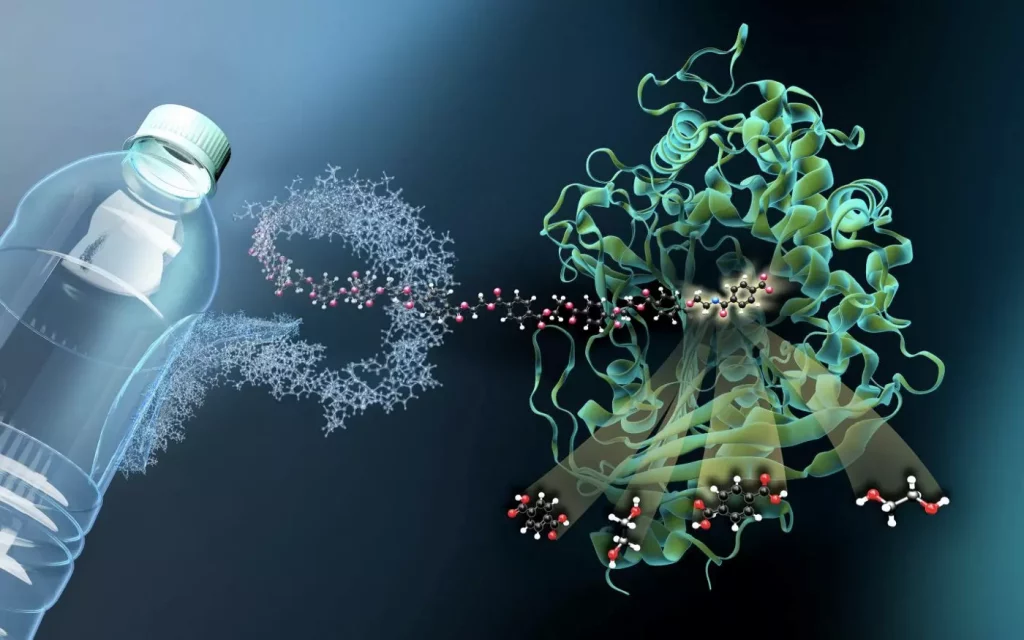
Because polyester is formed from petroleum, it’s very hard to recycle without losing quality. The concept behind polyester-eating microbes is to possess the microbes and eat down the polymer into its basic staple form. This way, it is often sold back to manufacturers. This process even works on garments made from mixed materials. This is typically a result of a less expensive and higher-quality thanks to recycling polyester and avoiding the utilization of petroleum to form a new fabric.
2. Recycling food waste into yarn.

For example, consider the assembly of juices, like fruit juice. Manufacturers have piles of garbage within the sort of seeds and peels. Some estimates have the quantity of garbage as high as 25 million tons per annum. One US-based startup, Circular Systems, is within the final testing phases of turning garbage into yarn. Supported by the citrus industry alone, this is able to eliminate a tremendous amount of food and fashion waste.
3. Algae-based fabric.

Traditional fabrics like cotton, have a huge carbon footprint. The water utilized in particular is exceptionally high in the production of cotton. Cotton also takes a while to grow, which suggests the utilization of insecticides and other chemicals has been significant within the traditional growing methods for cotton. Algae, on the opposite hand, grows quickly and doesn’t require extra water. It also frees up agriculture fields to supply other crops for food rather than clothing. Alga-Life is one startup currently working to show algae into fabric through an open-source process.
4. Turn cotton into new clothes.

Traditionally, cotton isn’t easy to recycle. Cotton clothing could be shredded and become insulation, but rarely does it become new clothing. However, a replacement process is allowing old cotton clothes to be dissolved in an eco-friendly solvent and then re-spend into new fibers. This eliminates both clothing waste and cotton-growing environmental problems. It’ll be a true win-win if it is often adopted on an outsized scale.
5. Create a database to trace wasted fabric on factory floors.

Estimates indicate that about 15 percent of cloth within the clothing production process finishes up trash on the manufacturing floor. A database to trace the wasted fabric would help another designer track and use it before turning to new fabrics.
What’s next for materiality and sustainable fashion?
Numerous startups are performing on ways to eliminate or lower the quantity of wasted material within the apparel industry. Many of those sustainable strategies are still within the testing phase and aren’t yet available on an outsized scale. But the subsequent are a number of the green leaders in the fight to make fashion production a more sustainable process.
Worn Again Technology may be a pioneering polymer recycling technology that will turn typically non-reusable textile and PET bottles back into new raw materials. This is able to create an endless cycle. Gr3n is another company experimenting with the new process of depolymerizing, to show PET and polyester textiles into new PET. This is able to save petroleum from getting used in the production of the latest materials. Carbios has developed an eco-friendly method to interrupt down PET into its original monomers by using enzymes. A bit like the opposite companies, this new process would eliminate the necessity to use more petroleum to supply new materials. Finally, Mango Materials produces PHB (poly-hydroxybutyrate) which is a biopolymer that has properties similar to polypropylene. PHB can be made into a variety of products, including electronic casings, children’s toys, shampoo bottles, and packaging, just to name a few.
In conclusion, the longer-term fashion must be one among sustainable materiality. New and innovative ways must be wont to recycle existing fabrics and lessen the environmental impact of the latest fibers.
Both Materiality and Sustainability are very near to each other. Thanks for reading and see you soon. Write us your valuable feedback from the contact box.
