Textile fiber and its properties are the key factors for textile processing. Moisture Regain and Moisture Content are important parameters for textile fiber, and directly affect physical properties. Moisture content is the rate of water in textile fiber, and regain is the moisture collecting % after drying. Here I present Moisture Regain, Moisture Content, their relation with textile fiber and the moisture regains percentage of different textile fibers.
Moisture Regain
Moisture regain is the amount of moisture that a material or product of textile fibers or yarn will absorb when exposed to a specific level of humidity. It is calculated as a percentage of the dry weight of the textile fiber. For example, if a textile fiber has a moisture regain of 8%, it means that it will gain 8% of its dry weight in moisture when exposed to the specific level of humidity used for the measurement.
Moisture Content
Moisture content is a measurement of the amount of moisture present in a textile fiber, it is also expressed as a percentage of the total weight of the fiber. It represents the weight of the water present in the fiber divided by the weight of the fiber when it is completely dry and multiplied by 100. Moisture content is important in textiles, and apparel, as it can affect the quality, strength, and safety of the final product. Textile fiber with high moisture content will be weaker, less elastic, and less flexible than fibers with less moisture content.
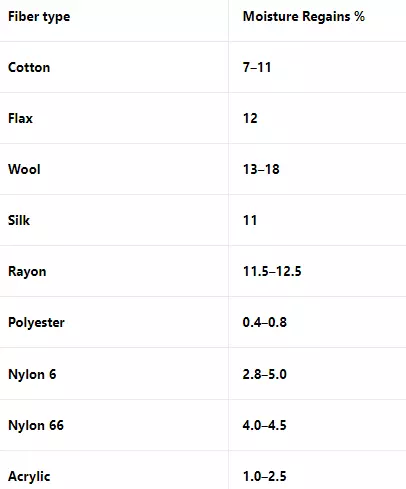
Moisture Regain % of Different Textile Fiber
| Fiber type | Moisture Regains % |
| Cotton | 7–11 |
| Flax | 12 |
| Wool | 13–18 |
| Silk | 11 |
| Rayon | 11.5–12.5 |
| Polyester | 0.4–0.8 |
| Nylon 6 | 2.8–5.0 |
| Nylon 66 | 4.0–4.5 |
| Acrylic | 1.0–2.5 |
| Modacrylic | 2.0–4.0 |
| Spandex | 0.75–1.3 |
Relation of Moisture Regain and Moisture Content with Textile Fiber
The moisture content of textile fibers is important for several reasons. First, moisture content becomes the factor in the physical properties of the fibers; those are strength, elasticity, and flexibility. Fibers with high moisture content will be weaker, less elastic, and less flexible than fibers with low moisture content. The performance of the finished textile product, the ability of a garment to withstand wear and tear. Second, moisture content reduces the dyeability of the fibers. Fibers with high moisture content are more difficult to dye than fibers with low moisture content. This is because the water in the fibers can interfere with the chemical reactions that take place during the dyeing process, resulting in uneven or inconsistent coloration. Third, moisture content can reduces the comfort of the textile product. Textiles with high moisture content can feel clammy and uncomfortable against the skin, while textiles with low moisture content can feel dry and scratchy. Finally, moisture content eases of processing the fibers into yarns and fabrics. High moisture content can cause fibers to stick together, making them difficult to spin or weave, while low moisture content can cause fibers to break or become brittle, making them difficult to process. So, it is very important to maintain the moisture content of textile fibers at an optimal level to ensure the desired properties of the final product.
The moisture regained from textile fibers is affected by the manufacturing process. Fibers with high moisture regain will absorb more moisture from the air, making them more comfortable to wear in humid environments, and more prone to shrinking and wrinkling. Fibers with low moisture regain, on the other hand, will absorb less moisture from the air, making them less shrink or wrinkle, and be less comfortable to wear in humid environments. For example, fibers that have been treated with a water-repellent finish have lower moisture regain than untreated fibers. Similarly, fibers that processing done with a flame-retardant make lower moisture regain than untreated fibers. It’s important to note that the moisture regained from textile fibers can vary depending on the type of fibers and the conditions under which they were measured. It’s common to find textile fibers with a moisture regain range between 3-11% it can vary depending on the type of fibers, the manufacturing process, and the intended use of the textile product.
You may love to read: Synthetic Fiber: Types, Manufacturer
Ref: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yarn_conditioning
