Applications of Nonwoven Fabric in Medical Textiles
Introduction
The application of nonwovens in the medical and healthcare sector goes back to the time of the Second World War when there was a high demand for new and large-capacity medical products. In many of the reports published it is stated that the nonwovens were regarded as the most effective product for bacterial barriers. They were also found to be better than the linens when it comes to the reduction of air-borne contamination. After the great development of nonwovens, they were manufactured in such a way that they serve medical needs and even proved to perform better than their woven counterparts in aspects of effectiveness, disability, etc. Here I present all the Applications of Nonwoven Fabric in Medical Textiles in below.
One of the biggest concerns in hospitals is cross-contamination, which was attributed majorly to the re-using of woven gowns, masks, and other similar products that would get contaminated and potentially spread the germs. The advancement in the nonwovens helped in the development of a more cost-effective option that was disposable and minimized the concern of cross-contamination.
What are the Medical Textiles have Applications of Nonwoven Fabric?
- Surgical gowns
- Surgical masks
- Surgical drapes and cover cloths
- Surgical hosiery
- Hospital ward textiles
- Cleaning products
- Wound care products
- Bandages
- Disposable feminine products
- Incontinence product
- Extracorporeal devices
- Plaster
- Surgical gloves
Details of Applications of Nonwoven Fabric in Medical Textiles Products
1. Surgical gowns
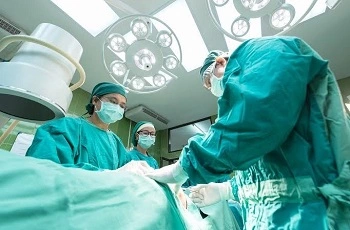
This is the most common application of nonwoven in Medical Textiles. Generally, surgical gowns are worn during medical operations, to stop contamination by plash of body fluids, for example, blood, respiratory secretions, vomit, or feces at the time of medical procedures. Disposable Surgical gowns are designed and manufactured with fluid-resistant materials to minimize the transfer of body fluids. These gowns are simply used to protect the wearer from the movement of microorganisms and only a small amount of body fluids.
2. Surgical masks
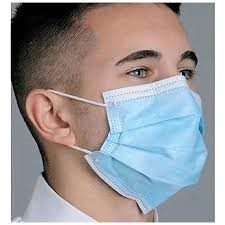
When it comes to surgical masks, they should possess attributes such as a high level of air permeability, and high filter capacity, and majorly should be lightweight and non-allergic. Generally, it consists of a very thin middle layer of extra fine glass fibers or synthetic microfibers covered on both sides by any of the methods, either an acrylic bonded parallel-laid or wet-laid non-woven. The mask is non-woven fabric in Medical textiles.
3 Surgical drapes and cover cloths
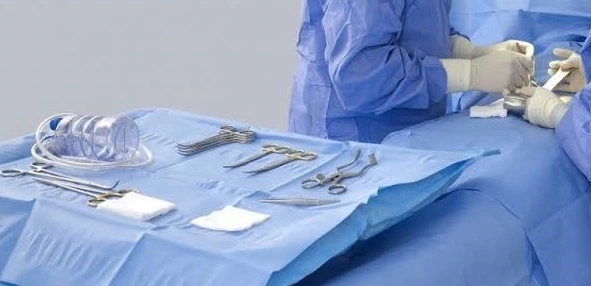
The products are specifically used to wrap cover patients or working areas around patients. The material used for this is particularly loop raised warp-knitted polyester fabric which is laminated with PTFE films to exhibit the properties of air permeability, comfort, and resistance to microbiological contaminants.
4. Surgical hosiery
These are simply graduated compression traits used for a wide variety of purposes, ranging from mild help for the limb to the recovery of dangerous disorders. Knee and elbow caps, which can be simply fashioned throughout knitting on round machines and might additionally consist of elastomeric threads are worn for help and compression throughout bodily energetic sports activities or for protection.
5. Hospital ward textiles
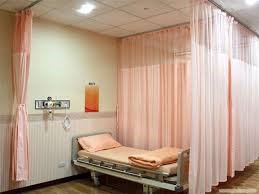
It includes applications such as bedding garb, bed covers, and incontinence merchandise which are used for the care and hygiene of patients. Now a days, the traditional woollen blankets had been changed to cotton leno woven blankets to reduce the threat of contamination and are manufactured from smooth spun two-fold yarns which own suited thermal qualities. Even, in isolation wards and in-depth care units, disposable defensive garb is worn to minimize pass contamination, which is made from a composite of tissue strengthened with a PET or polypropylene spunlaid web.
6. Cleaning products
These consist of products such as gauze for floors, dry dusting systems; hard surface disinfectant wipes that have high absorbency cloth, window cloth, electrostatic disposable dusters, cleaning mops, and many more.
7. Wound care products
In medical applications, the wound dressing is used for various purposes such as protection against infection, absorption and flow of blood and excess fluids, healing, and utilization of medication usually a wound dressing should be a kind of soft pliable pad for the wound to protect it from further injury, has the property to be easily applied and removed, should be sterile lint-free and nontoxic. The main thing to consider is that wound dressing should not stick to the wound and should have easy removal without disturbing new tissue growth. The latest wound dressing products are usually made of three layers-
- a. Wound contact layer: This layer should not adhere to the wound or cause itching of the skin if in the case dressing is not changed. It can be simply woven, knitted, or non-woven manufactured from silk, viscose, polyamide, or polyethylene.
- b. Middle absorbing layer: This layer should absorb blood or liquids that should provide a smoothing effect to protect the wound. It is generally manufactured from non-woven composed of cotton or viscose.
- c. Base Material: This layer provides a way by which the dressing is actually applied to the wound. The material used here, is coated with acrylic adhesive to grasp the dressing in place, eliminates the need for bandage.
When it comes to postoperative dressing, highly developed nonwoven structures such as perforated films on absorbent bases, polymers or nonwoven welded laminate and nonwoven are utilized. Polypropylene is used as the most unwettable fiber, but when converted to a fibrous web by melt blowing it may be wettable. So, in melt blowing a series of molten polymers is treated to blasts of air which create tiny fibrils that fall randomly as a web. Because of this, it becomes an absorbable dressing material. Conventionally, polypropylene is used in wound dressings either in fiber or fabric form, coupled with absorbent material.
8. Bandages
These are usually designed to perform a whole variety of specific functions reliant upon the medical requirement. They can be simply woven, knitted, nonwoven, or composite in structure. They can be generally categorized into different classes depending upon the function they are used. All are non-woven Fabrics in Medical Textiles.
- Simple bandages: These are normally fixation types of bandages that can be either elastic or inelastic in nature. Different kind of bandages such as adhesive bandage, cohesive bandages, and tubular bandages comes in this class.
- Light support bandages: These bandages are usually woven and are used for sprains or strains. Elastic crepe bandages are majorly been utilized for sprained wrist or ankle support. The elasticity properties of these bandages can be achieved by weaving cotton crepe yarns that have some twist content. The properties of stretch and recovery of these bandages apply proper tension to support the sprained limb.
- Compression bandages: These types of bandages are used to put a certain level of compression for the treatment and prevention of issues like deep vein thrombosis, leg ulceration and varicose veins. As per the compression they provide, compression bandages are categorized into light, moderate, high, and extra high compression bandages. They can be simply woven, warp and weft knitted from cotton and elastomeric yarns.
9. Disposable feminine products
It is simply made up of 3 layers,
- Inner pinnacle layer: It is manufactured from a mix of hydrophobic low-density fiber and it should be liquid and water permeable.
- Core layer: Made from full of wooden pulp and different absorbent fabrics, especially absorbent.
- Multi-layer barrier: This is usually water vapour permeable, however persistent to liquid water.
10. Incontinence product
The modern incontinence product is also made up from three layers. Cover stock which is usually permeable and diffuses liquid laterally. It has highly absorbent core and barrier polyethylene or PVC films that help patient cloths or bedding to keep it dry.
11. Extracorporeal devices
These are particularly mechanical organs that are used for blood purification and include the artificial kidney, the artificial liver, and the mechanical lung.
- Artificial kidney: It is a tiny instrument, about the size of a two-cell flashlight. It is made from hollow hair-sized cellulose fibers or sometimes hollow polyester fibers slightly later than capillary vessels. Fabric is being used to eliminate waste products from patient’s blood.
- Artificial device: It is made with hollow viscose material to segregate and dispose of patients’ plasma and supply fresh plasma.
- Artificial heart: It is generally an 8-ounce plastic pump lined with Dacom velour to minimize damage to blood and is a kind of chambered equipment about the size of a human heart. Silastic backing makes the fabric imperious to emerging gas that is not required in the blood.
- Mechanical lung: It is made from hollow polypropylene fiber or a hollow silicone membrane. Particularly used to remove carbon dioxide from a patient’s blood and supply fresh oxygen.
12. Plaster
Plasters are made up of three layers: 1) Plaster fabrics, 2) Adhesive, and 3) Wound pad.
Here, a simple plaster material comprised of gauze impregnated with plaster of Paris. The latest plaster fabric is manufactured from spun bonded nonwovens of cotton, viscose, polyester, or glass fiber. The adhesive which is being used for plaster fabric is acrylic because it doesn’t stick to the skin. The cushioning wound pad layer is made from knitted viscose fabric saturated with an antiseptic. The more the wound pad is absorbent, it helps in the rapid absorption of secretion from the wound.
13. Surgical gloves
It is an example of personal protective equipment used to shield the wearer and/or the patient from the transmission of micro-organisms that may highly cause infection or illness during medical procedures and examinations.
Medical gloves are considered as one part of an infection-control strategy. Medical gloves are disposable in nature and include various types like examination gloves, surgical gloves, and medical gloves for handling chemotherapy agents. Doctors use these medical gloves when they do treatment of patients where their hands may touch body fluids (such as blood, respiratory secretions, vomit, urine, or feces), certain hazardous drugs, or some potentially contaminated items.
Conclusion
Currently, it is very clearly visible that, the medical textile market is totally merged with nonwoven products. The reason behind it is, that their easy and quick modifiable properties and great performance have become crucial in this field. It is analyzed that the medical and Hygiene sectors are collaborating together to consume more than 90% of the total nonwoven production in the US. On the other side, in developing countries such as Asia, Africa and South America, need for medical nonwoven is increasing tremendously due to COVID 19 pandemic, fast-growing, increasingly urbanized, young, health-conscious population. In future, the need and applications of nonwovens in medical field is expected to grow very vast. These all are Applications of Nonwoven Fabric in Medical Textiles.
References
- https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/personal-protective-equipment-infection-control/medical-gloves
- https://www.fibre2fashion.com/industry-article/1292/nonwovens-for-medical-textiles?amp=true
- Applications of nonwovens in medical textiles, Asian Textile Journal 22(9):75-78, Srikrishnan Raghunathan, September 2013
- https://www.technicaltextile.net/articles/nonwovens-as-medical-textiles-3693
- Healthcare and Hygiene Products Application in Medical Textile
- Ramratan Guru, Anupam Kumar and Rohit Kumar
- https://www.edana.org/nw-related-industry/nonwovens-in-daily-life/medical-and-healthcare
- You may love to read: 8 Key Applications of Nonwoven Fabric
- Nonwoven Fabric Manufacturing Process: 3 Steps
- Classification of Medical Textile
- Recent Developments in Medical Textiles
- Top 20 Medical Textile Manufacturers /Companies in the World


