Wool is a natural fiber that is derived from the fleece of sheep and certain other animals, such as goats (cashmere and mohair), llamas, alpacas, and vicuñas. It is widely used in the textile industry for its excellent properties and versatility. Here are some key aspects of wool as a textile fiber. I present here the wool Manufacturing Process as Textile Fiber to Wool Fabric.
Wool Manufacturing Steps How does it become A Fabric?
- Shearing
- Skirting
- Cleaning
- Carding
- Combing
- Spinning
- Finishing
- Weaving/Knitting
- Finishing and Textile Production
Wool Manufacturing Process in Textile: From Fiber to Fabric
The manufacturing process of wool in textile fiber involves several steps, from shearing the sheep to producing yarn or fabric. Here is a general overview of the wool manufacturing process:
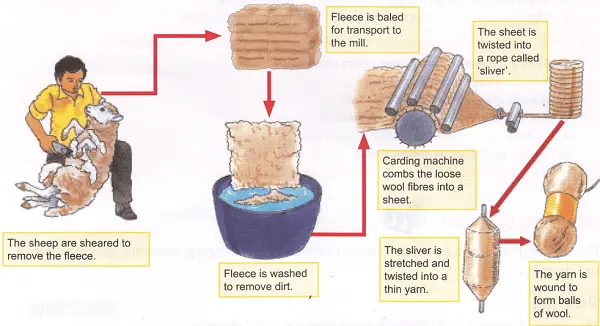
Shearing:
Sheep are sheared to remove their wool fleece. This process is usually done by professional shearers who use electric clippers to carefully remove the fleece while ensuring the sheep’s safety.
Skirting and Sorting
After shearing, the wool is sorted and graded based on its quality. Skirting involves removing the outer edges and any heavily soiled or undesirable portions of the fleece. Sorting is done to separate the wool based on factors such as fiber length, diameter, and color.
Cleaning:
The sorted wool is then thoroughly cleaned to remove dirt, grease, and other impurities. It goes through a process called scouring, which typically involves washing the wool in a detergent solution to remove oils and dirt. This step may be done using either mechanical or chemical methods.
Carding
Carding is the process of aligning the wool fibers and removing any remaining impurities or short fibers. It is done using large, rotating drums covered in wire teeth. The wool is fed into the carding machine, which combs and aligns the fibers into a thin web known as a carded sliver.
Combing (Optional)
In some cases, the carded sliver may undergo an additional process called combing. Combing removes shorter fibers, resulting in a smoother and more uniform yarn. This step is typically used for producing high-quality wool yarns.
Spinning
The carded or combed sliver is then spun into yarn. Spinning can be done using various methods, such as ring spinning, open-end spinning, or worsted spinning. The spinning process twists the fibers together to form a continuous strand of yarn.
Finishing:
After spinning, the wool yarn may undergo additional processes for finishing, depending on the intended final product. This can include steps such as dyeing, blending with other fibers, or further treatment to enhance its softness or durability.
Weaving/Knitting
The wool yarn is then used to create fabric through either weaving or knitting. Weaving involves interlacing the yarns at right angles on a loom, while knitting uses a series of interlocking loops formed with knitting needles or knitting machines.
Finishing and Textile Production:
The woven or knitted wool fabric undergoes finishing processes such as washing, dyeing, and fabric treatments to achieve the desired appearance and characteristics. It may also be cut and sewn into various textile products, including clothing, blankets, carpets, and upholstery.
Conclusion
Wool fabric has multiple uses in upholstery, carpeting, blankets, and winter jackets. Uncover the artistry and craftsmanship behind this age-old tradition, where nature’s finest fibers are harnessed to create warm, durable, and sustainable products. Delve into the wool manufacturing process and gain a deeper appreciation for the rich history, innovation, and creativity that goes into producing the softest, most versatile material known to humankind.
